In the world of search engine optimization (SEO), page indexing plays a crucial role in determining the visibility and success of a website.
Page indexing refers to the process by which search engines like Google crawl and include web pages in their search results.
Issues with page indexing can hinder the visibility of your website and impact your SEO efforts.
In this article, we will explore 6 common page indexing issues, their impact on your website's visibility, and practical strategies to resolve them.
How Search Engines Index Web Pages?
Search engines like Google use complex algorithms to crawl and index web pages. When a search engine's crawler visits a website, it analyzes the content and structure of each page defined in your website's sitemap file.
The crawler then adds the pages to its index, making them eligible to appear in search results when relevant queries are made.
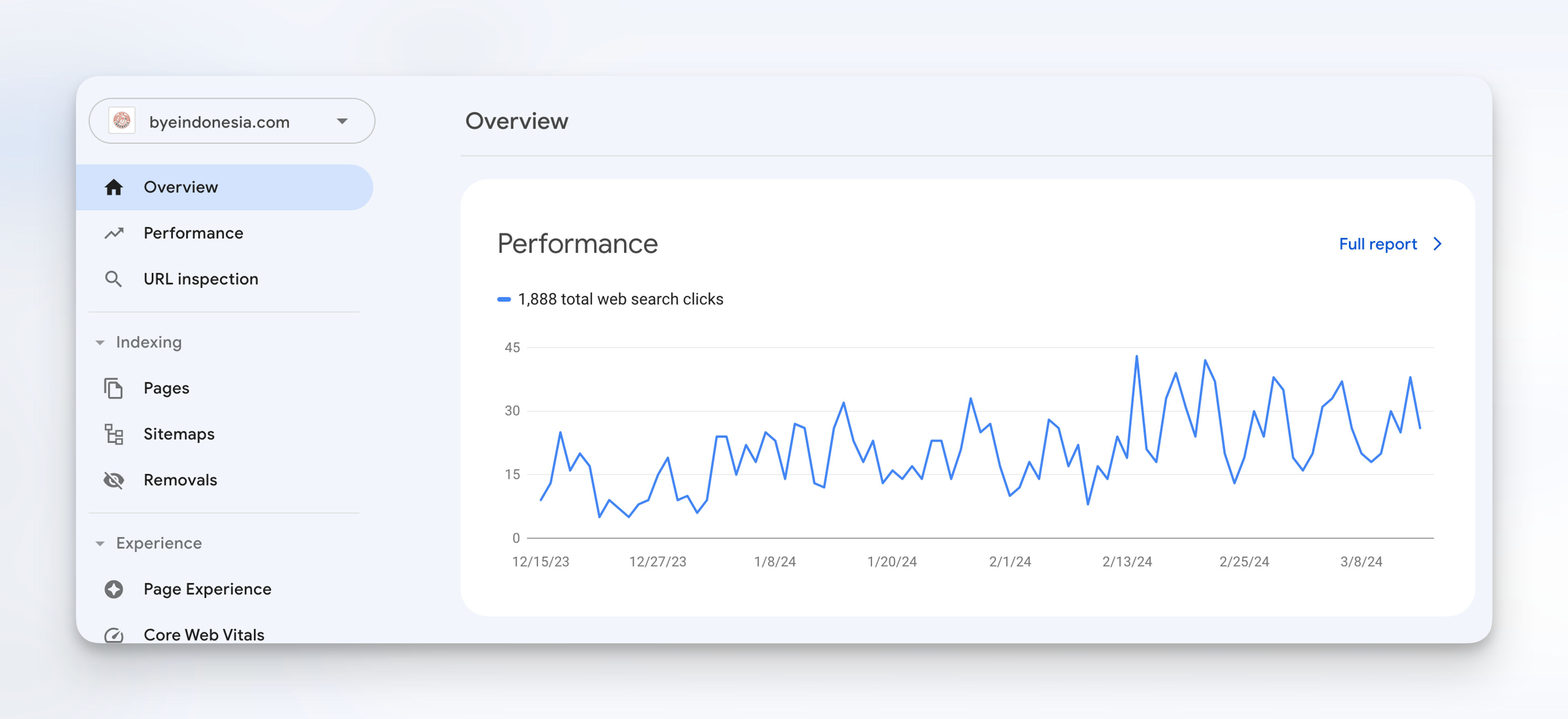
To see how it works, go to Google.com and type site:<domain name> in the search bar.
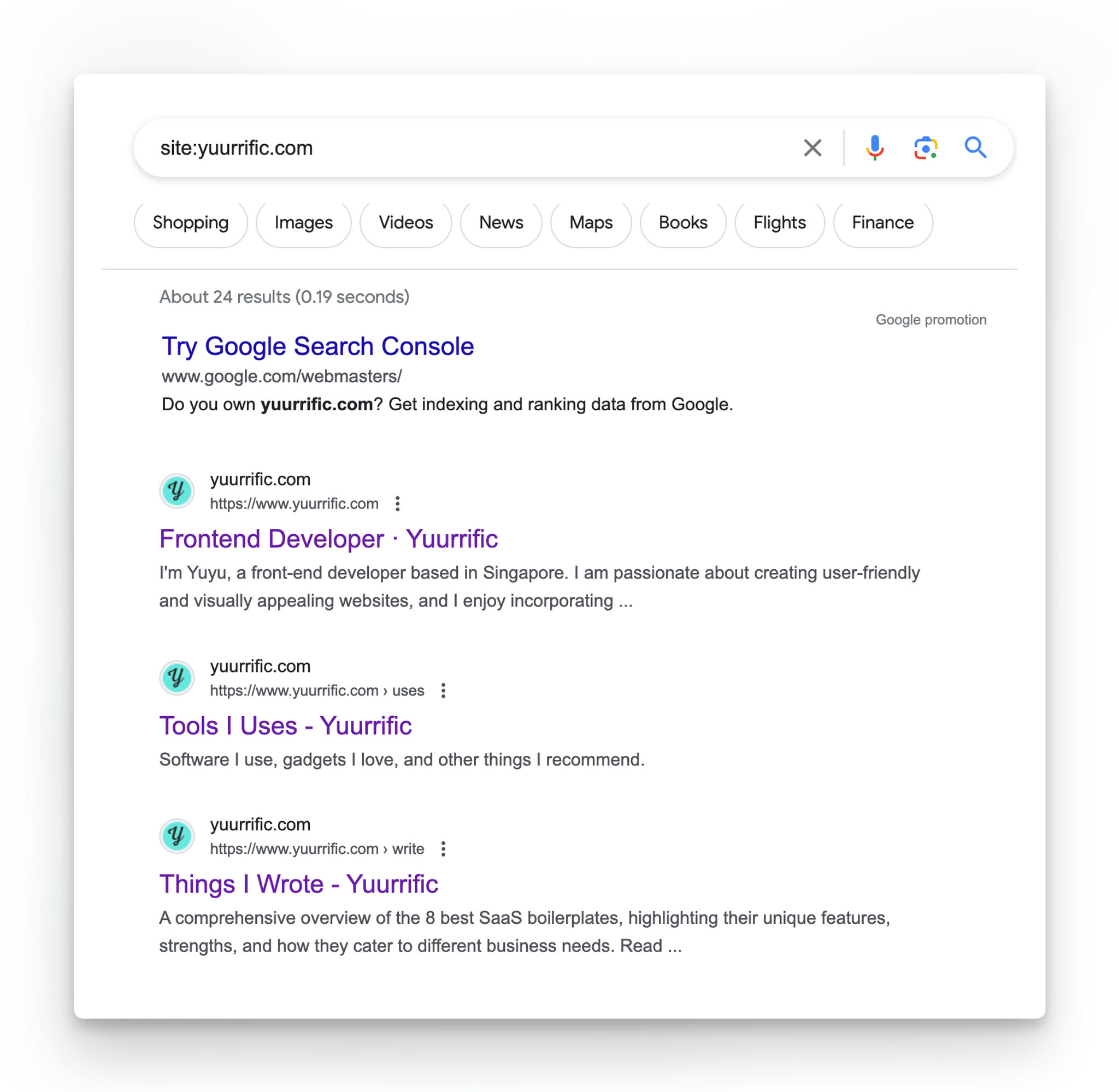
You should be able to see all the pages on the site that has been indexed by Google.
In the example above, that's what I see when I type site:yuurrific.com on the Google search bar.
6 Common Page Indexing Issues
1. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content refers to identical or very similar content that appears on multiple pages of a website. This can occur unintentionally, such as when multiple URLs lead to the same content, or intentionally, through content scraping or syndication.
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and dilute the relevance of your pages, leading to indexing issues as search engines struggle to determine which page to index.
How Duplicate Content Hurt SEO?
Having duplicate content on your site could hurt your SEO effort.
- Hurts your ranking: when you have multiple pages with similar content, Google might not be able to identify the original page you want to rank and that could hurt your page rank
- Hurts your outreach effort: When other website try to add a link to your site, they might link to the page you don't intend to rank. This would result with your backlinks distributes between all the pages with similar content.
- Hurts your crawling budget: Every website has a crawl budget based on your content popularity/staleness and crawl limit. When you have duplicated pages on your site, you're wasting your crawl budget because the search engine crawlers would crawl various version of the pages.
Common Causes of Duplicate Content
There are several common causes of duplicate content, not limited to:
-
URL Parameters: Dynamic URLs with parameters can create multiple versions of the same page, causing duplicate content.
-
WWW vs. Non-WWW: If your website is accessible with and without "www" at the beginning of the URLs, search engines might treat these different URL variations as 2 separate pages leading to duplicate content issue.
-
HTTP vs. HTTPS: Similar to "www", if user could access your site with both "HTTP" and "HTTPS" protocols, this could also lead to duplicate content.
-
Trailing Slashes vs. Non-Trailing Slashes: Search engines see variants of URLs with and without a trailing slash ("/") as duplicate content.
-
Content Scraping: When you copied content from another website and published it on your website without giving proper attribution, they could see it as dubplicate content.
How to Fix Duplicate Content Issues
To fix duplicate content issues and improve page indexing, consider the following strategies:
-
301 Redirects: Use 301 redirects to redirect duplicate URLs to the preferred version of the page. You could use 301 redirect to fix issues caused by trailing slashes
-
Canonical Tags: Implement canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a page when duplicate content exists.
-
Content Syndication: If you syndicate your content, ensure that the syndicated version includes a canonical tag pointing back to the original source.
2. Broken Links
Broken links, also known as dead links, are hyperlinks that lead to non-existent or inaccessible pages. Not found (404) issue can occur due to various reasons, such as page deletions, URL changes, or server errors.
Broken links not only impact user experience but also can prevent search engine crawlers from properly indexing your website.
What are the Impact of Broken Links on Page Indexing?
Broken links can have the following negative effects on page indexing:
-
Crawl Errors: Search engine crawlers encounter dead ends when they encounter broken links, preventing them from fully indexing your website.
-
Poor User Experience: Broken links frustrate users and can lead to a higher bounce rate, negatively impacting your website's visibility.
-
Loss of Backlinks: Broken links can result in the loss of valuable backlinks, which can affect your website's authority and ranking.
Methods to Identify and Fix Broken Links
To identify and fix broken links, consider the following methods:
-
Website Audit: Conduct a comprehensive website audit using tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to identify broken links. Check your sitemap and make sure affected URLs are written correctly.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitor your website for broken links and fix them promptly.
-
Proper Redirections: When deleting or moving pages, setup proper redirections (301 redirects) to ensure a seamless user experience and maintain link equity.
3. Slow Page Speed
Page speed refers to the time it takes for a web page to load completely. Slow-loading pages can frustrate users and negatively impact their experience on your website.
Additionally, slow page speed can also affect page indexing and overall website visibility.
How Page Speed Affects Page Indexing?
Page speed can impact page indexing in the following ways:
-
Crawl Budget: Search engine crawlers have a limited crawl budget, which determines how many pages they can crawl and index within a given timeframe. Slow-loading pages consume more of this budget, potentially leaving important pages unindexed.
-
User Experience: Slow page speed leads to a poor user experience, resulting in higher bounce rates and lower engagement metrics. These factors can indirectly affect page indexing and search engine rankings.
Techniques to Improve Page Speed
To improve page speed and enhance page indexing, consider implementing the following techniques:
-
Optimize Images: Compress and optimize images to reduce their file size without compromising quality.
-
Enable Browser Caching: Leverage browser caching to store static resources, such as CSS and JavaScript files, on the user's device, reducing load times for subsequent visits.
-
Minify CSS and JavaScript: Remove unnecessary characters and spaces from CSS and JavaScript files to reduce their file size.
-
Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): CDNs distribute your website's content across multiple servers worldwide, reducing the distance between the user and the server and improving page load times.
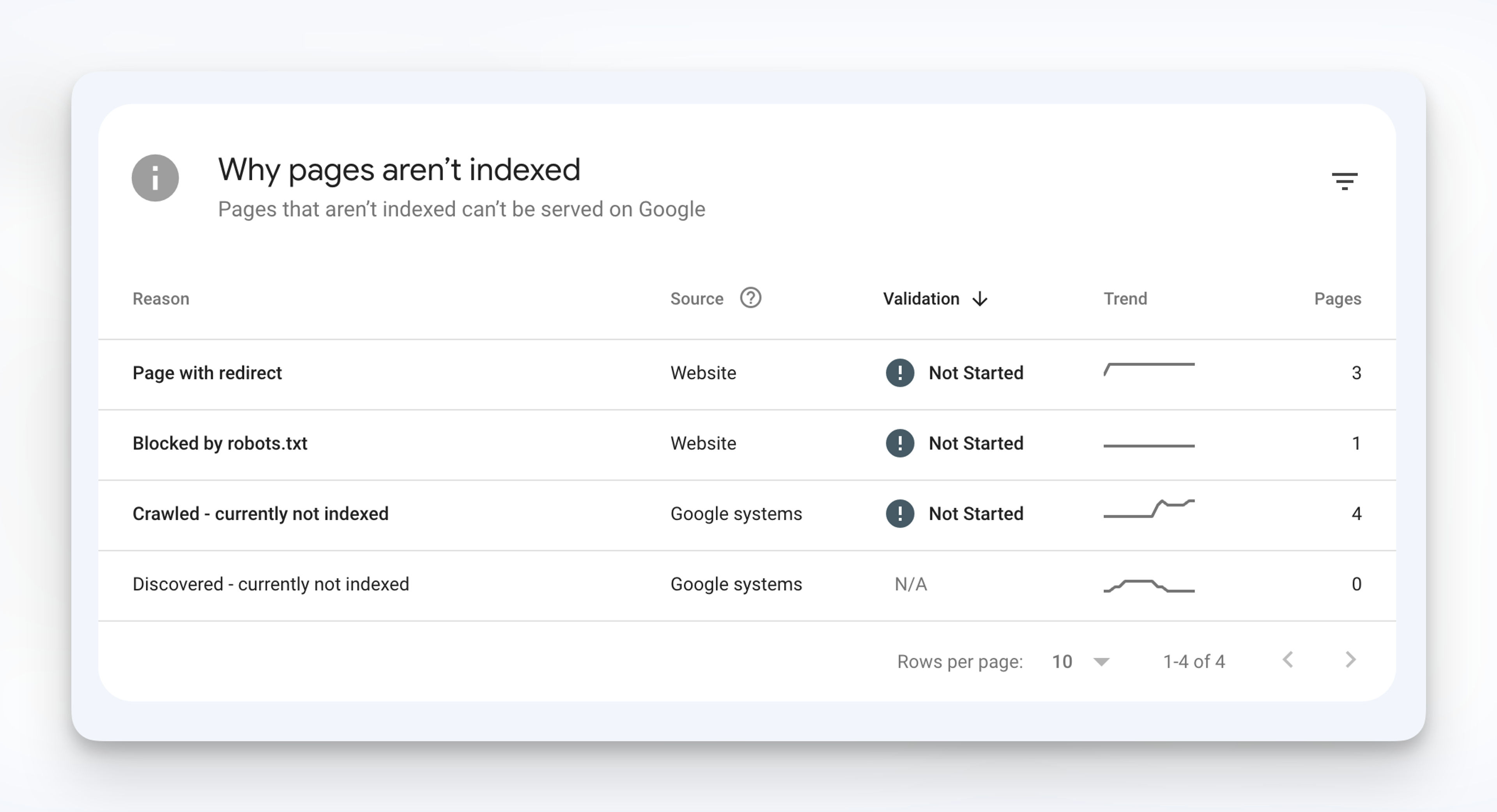
4. Incorrect Use of Robots.txt
The robots.txt file is a text file that instructs search engine crawlers on which pages to crawl and index.
Incorrectly blocking important pages or directories can prevent search engines from indexing them, resulting in decreased visibility.
Best Practices for Robots.txt Usage
To ensure proper page indexing, follow these best practices when using the robots.txt file:
-
Allow Important Pages: Ensure that important pages, such as your homepage and key landing pages, are not blocked in the robots.txt file.
-
Disallow Irrelevant Pages: Use the robots.txt file to disallow search engine crawlers from accessing irrelevant pages, such as login pages or admin sections.
-
Regularly Review and Update: Regularly review and update your robots.txt file to reflect changes in your website's structure or content.
5. XML Sitemap Errors
XML sitemaps provide search engine crawlers with a roadmap of your website.
It plays a crucial role in page indexing by helping search engine crawlers discover and understand the structure of your website.
A well-structured and error-free XML sitemap can improve the visibility and indexation of your pages.
Below are common XML sitemap issues that might lead to page indexing issues:
-
Missing Pages: Ensure that all important pages are included in the XML sitemap.
-
Incorrect URLs: Double-check that the URLs in the XML sitemap match the actual URLs of your web pages.
-
Duplicate URLs: Make sure you don't list down multiple variants of the same page to avoid duplicate content.
-
Invalid XML Format: Validate your XML sitemap using tools like XML Sitemap Validator to identify and fix any formatting errors.
6. Mobile-Friendly Issues
With the increasing use of mobile devices for browsing the internet, having a mobile-friendly website is crucial for both user experience and page indexing.
Impact of Mobile-Friendly Design on Page Indexing
Mobile-friendly design can impact page indexing in the following ways:
-
Mobile-First Indexing: Google's mobile-first indexing means that the mobile version of your website is prioritized for indexing. If your website is not mobile-friendly, it may not be indexed properly.
-
User Experience: A poor mobile experience can lead to higher bounce rates and lower engagement, indirectly affecting page indexing and search engine rankings.
Resolving Page Indexing Issues
Conducting a Site Audit
Conducting a comprehensive site audit is essential to identify and resolve page indexing issues. A site audit involves analyzing various aspects of your website, including technical SEO, content quality, and user experience.
Importance of Site Audits for Page Indexing
A site audit helps identify and resolve page indexing issues by:
-
Identifying Technical Issues: Site audits can uncover technical issues that may hinder page indexing, such as broken links, duplicate content, or incorrect use of meta tags.
-
Improving User Experience: A site audit allows you to identify and address user experience issues that may indirectly impact page indexing.
-
Optimizing Content: By analyzing your website's content, you can identify opportunities to optimize it for better indexing and search engine rankings.
Steps to Perform a Comprehensive Site Audit
To perform a comprehensive site audit and resolve page indexing issues, follow these steps:
-
Technical SEO Audit: Analyze your website's technical aspects, such as crawlability, URL structure, robots.txt usage, and XML sitemap implementation.
-
Content Audit: Evaluate the quality, relevance, and uniqueness of your website's content. Identify and address any duplicate content issues.
-
User Experience Audit: Assess your website's user experience, including page speed, mobile-friendliness, and navigation. Make improvements to enhance user experience and page indexing.
-
Backlink Audit: Analyze your website's backlink profile to identify any low-quality or spammy backlinks. Disavow or remove these links to improve your website's authority and indexing.
Conclusion
Page indexing issues can significantly impact your website's visibility and SEO efforts. By understanding the common page indexing issues and implementing the strategies outlined in this article, you can overcome these challenges and improve your website's indexation.
Conducting regular site audits, resolving duplicate content and broken links, optimizing page speed, and ensuring mobile-friendliness are crucial steps in resolving page indexing issues.
By taking a proactive approach to resolve page indexing issues and implementing SEO best practices, you can enhance your website's visibility, attract more organic traffic, and achieve better search engine rankings.